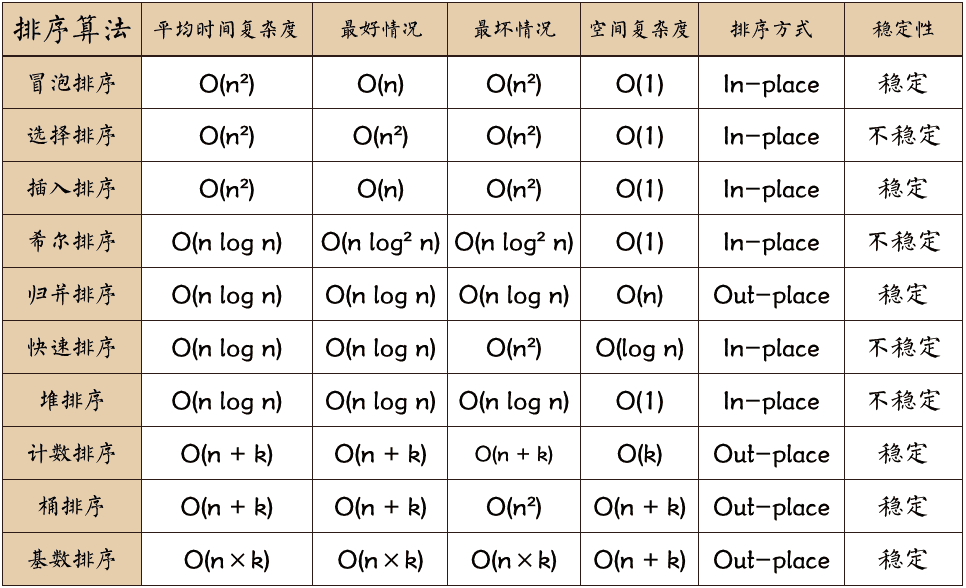
本文用C++阐述十大排序算法的升降序实现方法。
交换排序(冒泡,快排)
插入排序(简单插入,希尔)
选择排序、堆排序
归并排序
基数排序,计数排序,桶排序
开篇前先将随机数生成函数与打印容器的函数对象置于此
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 void printVec (T val) cout << val << " " ; } template <class T>void randData (vector<T>& a, int n,int random=99 ) a.resize (n); srand (time (NULL )); if (typeid (T) == typeid (char )) { for (int i = 0 ;i < n;i++) { a[i] = 'a' + rand () % 26 ; cout << a[i] << "," ; } } else if (typeid (T) == typeid (int )) { for (int i = 0 ;i < n;i++) { a[i] = rand () % random; cout << a[i] << "," ; } } else if (typeid (T) == typeid (double )) { uniform_real_distribution<double > u (-1 , 1 ); default_random_engine e (time(NULL )) ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { cout << u (e) << " " ; } } cout << endl; }
比较排序
比较排序(Comparison Sort)通过对数组中的元素进行比较来实现排序。
动画演示平台 Comparison Sorting Visualization (usfca.edu)
交换排序
冒泡排序
稳定
时间复杂度最好为 O(n) O(n2 ) O(n2 )
空间复杂度 O(1)
原地算法
思路
从左到右,依次比较相邻的元素大小,更大(小)的元素交换到右边。类似水中的气泡一样,先让大(小)的元素浮上去。
tip 用一个布尔类型变量充当哨兵,如果一趟遍历没有任何元素发生交换,说明该数列已经有序。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 template <class T>void bubbleSort (vector<T>& nums, bool is_increase = true ) bool guard = true ; if (is_increase) { for (int i = 0 ;i < nums.size () - 1 ;i++) { guard = true ; for (int j = 0 ;j < nums.size () - (i + 1 );j++) { if (nums[j] > nums[j + 1 ]) { guard = false ; T tmp = nums[j]; nums[j] = nums[j + 1 ]; nums[j + 1 ] = tmp; } } if (guard) return ; } } else { for (int i = 0 ;i < nums.size () - 1 ;i++) { guard = true ; for (int j = 0 ;j < nums.size () - (i + 1 );j++) { if (nums[j] < nums[j + 1 ]) { guard = false ; T tmp = nums[j]; nums[j] = nums[j + 1 ]; nums[j + 1 ] = tmp; } } if (guard) return ; } } }
测试
1 2 3 4 5 vector<int > nums ; randData (nums, 30 );bubbleSort <int >(nums,0 );bubbleSort <int >(nums);for_each(nums.begin (), nums.end (), printVec<int >);
快速排序
不稳定
最坏情况发生在数据有序情况下,时间复杂度为O(n2 )
平均时间复杂度和最好情况时间复杂度均为O(n*log n)
空间复杂度O(n*log n)
原地算法
思路
选取数组第一个元素作为基准
依次从右向左挑选一个比基准数值小的元素和从左到右挑选一个比基准数值大的元素,并交换位置。最终使得数据值比基准大的放在基准元素左边,数值比基准小的放在基准元素右边。基准元素置于中间。
递归地把小于基准值元素的子数列和大于基准值元素的子数列按上述方法排序
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 template <class T>int partition (vector<T>& nums, int low, int high, bool is_increase) T pivot = nums[low]; if (is_increase) { while (low < high) { while (low < high && nums[high] >= pivot)high--; nums[low] = nums[high]; while (low < high && nums[low] <= pivot)low++; nums[high] = nums[low]; } nums[low] = pivot; } else { while (low < high) { while (low < high && nums[high] <= pivot)high--; nums[low] = nums[high]; while (low < high && nums[low] >= pivot)low++; nums[high] = nums[low]; } nums[low] = pivot; } return low; } template <class T>void qSort (vector<T>& nums, int low, int high, bool is_increase = true ) if (low < high) { int pivot = partition (nums, low, high, is_increase); qSort (nums, low, pivot - 1 , is_increase); qSort (nums, pivot + 1 , high, is_increase); } else return ; }
测试
1 2 3 4 5 vector<int > nums ; randData (nums, 30 );qSort <int >(nums, 0 , nums.size () - 1 , 0 );qSort <int >(nums, 0 , nums.size () - 1 );for_each(nums.begin (), nums.end (), printVec<int >);
插入排序
简单插入排序
稳定
O(n2 ) O(n) O(1) 原地算法
思路
将第一待排序序列第一个元素看做一个有序序列,把第二个元素到最后一个元素当成是未排序序列。
从头到尾依次扫描未排序序列,将扫描到的每个元素与有序序列的每个元素进行比较,小于哪个有序序列的元素就进行交换,相当于插入到该元素索引位置。
tip 容器的第一个元素可以默认为有序序列,所以第一层循环可以从i=1出发
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 template <class T>void insertSort (vector<T>& nums, bool is_increase = true ) T tmp; int j; if (is_increase) { for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.size (); i++) { tmp = nums[i]; for (j = i; j > 0 && nums[j - 1 ] > tmp; j--) nums[j] = nums[j - 1 ]; nums[j] = tmp; } } else { for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.size (); i++) { tmp = nums[i]; for (j = i; j > 0 && nums[j - 1 ] < tmp; j--) nums[j] = nums[j - 1 ]; nums[j] = tmp; } } }
测试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 vector<int > nums ; cout << "原始数据:" << endl; randData (nums, 30 );insertSort <int >(nums,0 );cout << "降序数据:" << endl; for_each(nums.begin (), nums.end (), printVec<int >); insertSort <int >(nums);cout << endl<<"升序数据:" << endl; for_each(nums.begin (), nums.end (), printVec<int >);
希尔排序
1959年Shell发明,第一个突破 O(n2) 的排序算法,是插入排序的改进版。它与插入排序的不同之处在于,它会优先比较距离较远的元素。希尔排序又叫缩小增量排序 。
不稳定
平均时间复杂度O(n1.3 ) O(n) O(n2 )
空间复杂度O(1)
原地算法
思路
选择一个增量序列 t1,t2,…,tk,其中 ti>tj,tk=1;
按增量序列个数 k,对序列进行 k 趟排序;
每趟排序,根据对应的增量 ti,将待排序列分割成若干长度为 m 的子序列,分别对各子表进行直接插入排序。仅增量因子为 1 时,整个序列作为一个表来处理,表长度即为整个序列的长度。
tip 最简单的思路就是先按照插入排序写,在外层再套一层循环,使步长坐标处的元素按照步长间距来进行插入排序。
参照 4希尔排序代码_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
每次交换的时候就不会像冒泡排序一样每次只能在相邻的数之间进行交换,交换的距离就大的多了。因此总的比较和交换次数就少了,速度自然就提高了。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 template <class T>void shellSort (vector<T>&nums, bool is_increase = true ) T tmp; int j; if (is_increase) { for (int step = nums.size () / 2 ;step;step /= 2 ) { for (int i = step;i < nums.size ();i++) { tmp = nums[i]; for (j = i;j >= step && nums[j - step] > tmp;j -= step) { nums[j] = nums[j - step]; } nums[j] = tmp; } } } else { for (int step = nums.size () / 2 ;step;step /= 2 ) { for (int i = step;i < nums.size ();i++) { tmp = nums[i]; for (j = i;j >= step && nums[j - step] < tmp;j -= step) { nums[j] = nums[j - step]; } nums[j] = tmp; } } } }
测试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 vector<int > nums ; cout << "原始数据:" << endl; randData (nums, 30 );shellSort <int >(nums,0 );cout << "降序数据:" << endl; for_each(nums.begin (), nums.end (), printVec<int >); insertSort <int >(nums);cout << endl<<"升序数据:" << endl; for_each(nums.begin (), nums.end (), printVec<int >);
选择排序
简单选择排序
不稳定
时间复杂度最好最坏平均都为 (n2 )
空间复杂度O(1)
原地算法
每一趟n-i+1(i=1,2,…,n-1)个记录中选取值最小的索引作为有序序列的第 i 个索引。
思路
在未排序序列中找到最小(大)元素,存放到排序序列的起始位置;
在剩余未排序元素中继续寻找最小(大)元素,放到已排序序列的末尾;
重复步骤 2,直到所有元素排序完毕。
tip 因为每一趟便将一个元素放到正确的位置上,所以当容器中的n-1个元素已经归位时,此时容器已经是有序数列了。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 template <class T>void selectSort (vector<T>& nums, bool is_increase = true ) int min_index; int max_index; T tmp; if (is_increase) { for (int i = 0 ;i < nums.size () - 1 ;i++) { min_index = i; for (int j = i + 1 ;j < nums.size ();j++) { if (nums[j] < nums[min_index]) min_index = j; } tmp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[min_index]; nums[min_index] = tmp; } } else { for (int i = 0 ;i < nums.size () - 1 ;i++) { max_index = i; for (int j = i + 1 ;j < nums.size ();j++) { if (nums[j] > nums[max_index]) max_index = j; } tmp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[max_index]; nums[max_index] = tmp; } } }
测试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 vector<int > nums ; cout << "原始数据:" << endl; randData (nums, 30 );selectSort <int >(nums,0 );cout << "降序数据:" << endl; for_each(nums.begin (), nums.end (), printVec<int >); selectSort <int >(nums);cout << endl<<"升序数据:" << endl; for_each(nums.begin (), nums.end (), printVec<int >);
堆排序
动画展示 Heap Sort Visualization (usfca.edu)
不稳定,适合数据量较大的序列
时间复杂度最好最坏平均都为O(n*log n)
空间复杂度O(1)
原地算法
思路
将初始待排序关键字序列(R1,R2….Rn)构建成大顶堆,此堆为初始的无序区;
将堆顶元素R[1]与最后一个元素R[n]交换,此时得到新的无序区(R1,R2,……Rn-1)和新的有序区(Rn),且满足R[1,2…n-1]<=R[n];
由于交换后新的堆顶R[1]可能违反堆的性质,因此需要对当前无序区(R1,R2,……Rn-1)调整为新堆,然后再次将R[1]与无序区最后一个元素交换,得到新的无序区(R1,R2….Rn-2)和新的有序区(Rn-1,Rn)。不断重复此过程直到有序区的元素个数为n-1,则整个排序过程完成。
堆积内部是完全二叉树的结构,并且用数组存放。所以可以根据父节点坐标求出子节点的坐标。设父节点坐标为i(从0开始),则左孩子2 * i + 1,右孩子2 * i + 2。也可以通过孩子结点反推出父节点下标,设孩子结点为j,则 i=(j-1)/2,因为整数÷2会舍弃小数,所以不需要区分左右孩子情况。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 template <class T>void adjustHeap (vector<T>& heap,int root,int end,bool is_increase) if (root*2 +1 > end)return ; T tmp; int left = 2 * root + 1 ; int right = 2 * root + 2 ; int max_or_min; if (is_increase) { if (right < end) max_or_min = heap[left] > heap[right] ? left : right; else max_or_min = left; if (heap[root] < heap[max_or_min]) { tmp = heap[max_or_min]; heap[max_or_min] = heap[root]; heap[root] = tmp; adjustHeap (heap, max_or_min, end, is_increase); } } else { if (right < end) max_or_min = heap[left] < heap[right] ? left : right; else max_or_min = left; if (heap[root] > heap[max_or_min]) { tmp = heap[max_or_min]; heap[max_or_min] = heap[root]; heap[root] = tmp; adjustHeap (heap, max_or_min, end, is_increase); } } } template <class T>void buildHeap (vector<T>& heap, int end, bool is_increase) for (int i = (end - 1 ) / 2 ;i >= 0 ;i--) { adjustHeap (heap, i, end, is_increase); } } template <class T>void heapSort (vector<T>& heap, bool is_increase=true ) T tmp; buildHeap (heap, heap.size () - 1 , is_increase); for (int i = heap.size () - 1 ;i;i--) { tmp=heap[i]; heap[i] = heap[0 ]; heap[0 ] = tmp; buildHeap (heap, i-1 , is_increase); } }
测试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 vector<int > nums ; cout << "原始数据:" << endl; randData (nums, 30 );heapSort <int >(nums,0 );cout << "降序数据:" << endl; for_each(nums.begin (), nums.end (), printVec<int >); heapSort <int >(nums);cout << endl<<"升序数据:" << endl; for_each(nums.begin (), nums.end (), printVec<int >);
归并排序
稳定
时间复杂度平均最坏最好均为O(n*logn)
空间复杂度O(n)
非原地算法,占用额外空间
思路
把长度为 n 的输入序列分成两个长度为 n/2 的子序列;
对这两个子序列分别采用归并排序;
将两个排序好的子序列合并成一个最终的排序序列。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 template <class T>void merge (vector<T>& nums, int left, int right, int mid, bool is_increase) vector<T> left_vec; vector<T> right_vec; left_vec.resize (mid - left + 1 ); right_vec.resize (right - mid); for (int i = 0 ;i < right_vec.size ();i++) { left_vec[i] = nums[left + i]; right_vec[i] = nums[i + mid+ 1 ]; } left_vec[mid - left] = nums[mid]; int i = 0 ; int j = 0 ; while (is_increase && i < left_vec.size () && j < right_vec.size ()) nums[left++] = left_vec[i] < right_vec[j] ? left_vec[i++] : right_vec[j++]; while (!is_increase && i < left_vec.size () && j < right_vec.size () ) nums[left++] = left_vec[i] > right_vec[j] ? left_vec[i++] : right_vec[j++]; while (i < left_vec.size ())nums[left++] = left_vec[i++]; while (j < right_vec.size ())nums[left++] = right_vec[j++]; } template <class T>void mergeSort (vector<T>& nums, bool is_increase = true ,int start=0 , int end=-1 ) if (end == -1 )end = nums.size () - 1 ; if (start == end)return ; int mid = (start + end) / 2 ; mergeSort (nums, is_increase, start, mid); mergeSort (nums, is_increase , mid+1 , end); merge (nums, start, end, mid, is_increase); }
测试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 vector<int > nums ; cout << "原始数据:" << endl; randData (nums, 30 );mergeSort <int >(nums,false );cout << "降序数据:" << endl; for_each(nums.begin (), nums.end (), printVec<int >); mergeSort <int >(nums, true ,5 ,25 );cout << endl << "局部升序数据:" << endl; for_each(nums.begin (), nums.end (), printVec<int >); mergeSort <int >(nums,true );cout << endl << "升序数据:" << endl; for_each(nums.begin (), nums.end (), printVec<int >); mergeSort <int >(nums, false , 5 , 25 );cout <<endl<< "局部降序数据:" << endl; for_each(nums.begin (), nums.end (), printVec<int >);
非比较排序
非比较排序分为三种,桶排序,计数排序和基数排序。
桶排序
动画展示 Bucket Sort Visualization (usfca.edu)
桶排序 (Bucket sort)是计数排序的升级版。它利用了函数的映射关系,高效与否的关键就在于这个映射函数的确定。桶排序的工作的原理:假设输入数据服从均匀分布,将数据分到有限数量的桶(一定的区间范围)里,每个桶再分别排序(有可能再使用别的排序算法或是以递归方式继续使用桶排序进行排)
桶排序是稳定排序 ,但仅限于桶排序本身,假如桶内排序采用了快速排序之类的非稳定排序,那么就是不稳定的。
时间复杂度最好情况O(n+k) O(n2 )
空间复杂度O(n+k)
思路
设置一个定量的数组当作空桶;
遍历输入数据,并且把数据一个一个放到对应的桶里去;
对每个不是空的桶进行排序;
从不是空的桶里把排好序的数据拼接起来。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 template <class T>void bucketSort (vector<T>&nums,int bucket_size ,void (*func)(vector<T>&,bool ), bool is_increase = true ) if (nums.size () == 0 )return ; T max=nums[0 ], min=nums[0 ]; for (auto num : nums) { if (num > max)max = num; if (num < min)min = num; } int bucket_range = (max - min+1 ) / bucket_size + 1 ; vector< vector<T> > bucket (bucket_size); for (auto num : nums) bucket[(num - min) / bucket_range].push_back (num); for (int i = 0 ;i < bucket_size;i++) func (bucket[i], is_increase); int index = 0 ; if (is_increase) for (auto arr : bucket) for (auto data : arr) nums[index++] = data; else for (int i = bucket.size () - 1 ;i >= 0 ;i--) for (auto data : bucket[i]) nums[index++] = data; }
测试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 using type = char ;vector<type> nums ; cout << "原始数据:" << endl; randData (nums, 30 );bucketSort <type>(nums,4 ,shellSort);cout << "升序数据:" << endl; for_each(nums.begin (), nums.end (), printVec<type>); cout << endl<<"降序数据:" << endl; bucketSort <type>(nums, 4 , countSort,0 );for_each(nums.begin (), nums.end (), printVec<type>);
计数排序
动画展示 Counting Sort Visualization (usfca.edu)
适用于量大但是数的取值范围区间小的情况
稳定,升序的计数数组按从前到后的方式累加,所以计数数组的元素值从前至后增大;反向取数,可以同样大小的数后出现的在靠后的位置,保持了排序的稳定性。而降序,相同大小的值a、b,若a在b的左边,降序排列后a应在b的右边以保持稳定性。降序的计数数组按从后到前的方式累加,所以计数数组的元素值从前至后减小;越早出现的元素应在降序中是更靠后的位置,所以降序应当从前到后取数。结合代码理解
时间复杂度 O(n+k)
空间复杂度 O(n+k)
非原地算法
tips k为计数数组的长度
思路
找出待排序的数组中最大和最小的元素;
统计数组中每个值为 i 的元素出现的次数,存入数组 C 的第 i 项;
对所有的计数累加(从 C 中的第一个元素开始,每一项和前一项相加);
反向填充目标数组:将每个元素i放在新数组的第 C(i) 项,每放一个元素就将 C(i) 减去 1。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 template <class T>vector<T> countSort_pre (vector<T> nums, bool is_increase) { if (nums.size () == 0 )return nums; if (typeid (T) != typeid (int ) && typeid (T) != typeid (short ) && typeid (T) != typeid (char )&&typeid (T) != typeid (long )) { throw "计数排序只能排序整型和字符型数据" ; } T min = nums[0 ], max = nums[0 ]; for (auto num : nums) { if (num > max)max = num; if (num < min)min = num; } vector<int >counting; vector<T>tmp; counting.resize (max - min + 1 ,0 ); tmp.resize (nums.size ()); for (auto num : nums) counting[num - min]++; if (is_increase) { for (int i = 1 ;i < counting.size ();i++) counting[i] += counting[i - 1 ]; for (int i = nums.size () - 1 ;i >= 0 ;i--) tmp[--counting[nums[i] - min]] = nums[i]; } else { for (int i = counting.size ()-2 ;i>=0 ;i--) counting[i] += counting[i + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ;i <nums.size ();i++) tmp[--counting[nums[i] - min]] = nums[i]; } return tmp; } template <class T>void countSort (vector<T>& nums, bool is_increase=true ) try { nums=countSort_pre (nums,is_increase); } catch (const char * msg) { cerr << msg << endl; } }
测试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 using type = char ;vector<type> nums ; cout << "原始数据:" << endl; randData (nums, 30 );countSort <type>(nums);cout << "升序数据:" << endl; for_each(nums.begin (), nums.end (), printVec<type>); cout << "降序数据:" << endl; countSort <type>(nums,0 );for_each(nums.begin (), nums.end (), printVec<type>);
基数排序
动画展示 Radix Sort Visualzation (usfca.edu)
稳定
时间复杂度 O(n*k)
空间复杂度 O(n+k)
思路
取得数组中的最大数,并取得位数;
arr 为原始数组,从最低位开始取每个位组成 radix 数组;
对 radix 进行计数排序(利用计数排序适用于小范围数的特点)。